Atopic Dermatitis FAQ
What is atopic dermatitis?
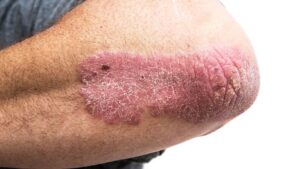
Atopic dermatitis is a skin condition. A person with this condition has skin that becomes extremely itchy. Scratching leads to redness, swelling, cracking, “weeping” clear fluid, crusting and scaling. Often, the skin gets worse (flares), and then it improves or clears up (remissions). Atopic dermatitis is the most common kind of eczema, a term that describes many kinds of skin problems.
Who gets atopic dermatitis?
It is most common in babies and children, but it can happen to anyone. People who live in cities and dry climates may be more likely to get this condition. You can’t “catch” it or give it to other people.
What are the symptoms?
The most common symptoms of atopic dermatitis are:
- Dry and itchy skin
- Rashes on the face, inside the elbows, behind the knees and on the hands and feet
Scratching the skin can cause:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Cracking
- “Weeping” clear fluid
- Crusting
- Thick skin
- Scaling
What causes it?
No one knows what causes atopic dermatitis. It is probably passed down from your parents (genetics). Your environment can also trigger symptoms. Stress can make the condition worse, but it does not cause the condition.
Is there a test for it?
Currently, there is no single test to diagnose atopic dermatitis, but your doctor may ask you about your medical history, including your family history of allergies, and whether you have hay fever or asthma. Also, exposure to irritants, including:
- Wool or synthetic fibers
- Soaps and detergents
- Some perfumes and cosmetics
- Substances such as chlorine, mineral oil, or solvents
- Dust or sand
- Cigarette smoke
Additionally, the doctor will ask you about:
- Sleep problems
- Foods that seem to be related to skin flares
- Previous treatments for skin-related symptoms
- Use of steroids or other medications
How is it treated?
The goals in treating atopic dermatitis are to heal the skin and prevent flares. You should watch for changes in the skin to find out what treatments help the most. These can include:
- Skin creams or ointments that control swelling and lower allergic reactions
- Corticosteroids
- Antibiotics to treat infections caused by bacteria
- Antihistamines that make people sleepy to help stop nighttime scratching
- Drugs that suppress the immune system
The doctor may also recommend:
- Light therapy
- Skin care that helps heal the skin and keep it healthy
- Avoiding things that cause an allergic reaction
Living with atopic dermatitis
Besides medications, there are a number of things you can do to help control your atopic dermatitis. Skin care is most important, including:
- Taking lukewarm baths to cleanse and moisturize the skin without drying it out
- Using mild bar soap or nonsoap cleanser
- Gently patting the skin dry after bathing
- Applying a moisturizer to seal in the water after bathing
- Using creams and ointments — and avoid lotions with high water or alcohol content
- Protecting the skin from rough clothing, such as wool or man-made fibers
Stay away from things you are — or can be — allergic to, such as:
- Dust mites
- Molds
- Pollen
- Cat or dog dander
- Some perfumes and makeup
- Certain foods such as eggs, peanuts, milk, fish, soy products, or wheat
Above all, prevent scratching or rubbing, which irritates the skin, increases swelling, and actually increases itchiness. Keep your child’s fingernails short to help reduce scratching.
If you exhibit any of the above symptoms, make sure to get your skin checked out by a professional. Schedule an appointment with DeSilva Dermatology today.

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post