Understanding Hyperhidrosis
What is hyperhidrosis?
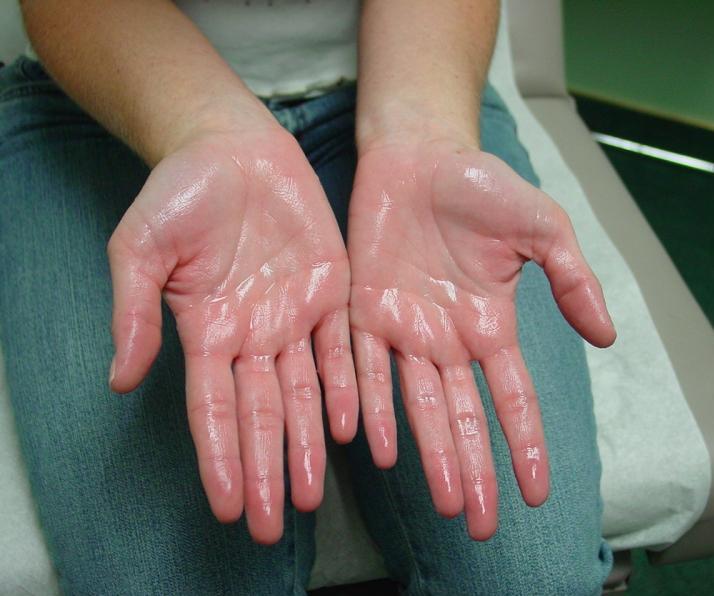
Hyperhidrosis is characterized as excessive sweating that is not related to heat or physical exertion. A person with this condition can sweat so much that it stains their clothing. It can cause acute social embarrassment. It usually on the the hands, feet, underarms or face, on both sides of the body.
What causes it?
Normally, the human body sweats when it needs to cool itself on a hot day, after physical exertion or as a nervous reaction. With hyperhidroisis, however, the triggers are completely different.
The most prevalent form of hyperhidrosis is known as primary focal (essential) hyperhidrosis. With this condition, the nerves responsible for signaling your sweat glands become overactive, even though they haven’t been triggered by the causes listed above. However, stress and nervousness can make it worse.
There is no known medical cause for this type of hyperhidrosis. It may have a hereditary component, however, because it sometimes seems to run in families.
Another form of hyperhidrosis, known as secondary hyperhidrosis, occurs when the excess sweat is caused by a medical condition. Though it’s a less common type it’s more likely to cause sweating all over your body. Medical conditions that can lead to secondary hyperhidrosis include:
- Diabetes
- Menopause (hot flashes)
- Thyroid problems
- Low blood sugar
- Certain types of cancer
- Heart attack
- Nervous system disorders
- Infections
If your sweating is accompanied by lightheadedness, chest pain or nausea, see a medical professional immediately.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history during your appointment. A physical exam or lab tests my also be in order. Blood, urine or other lab tests may be in order to see if the sweating is caused by other conditions, such as low blood sugar or an overactive thyroid,
Sweat tests may also be conducted to determine how severe the condition is. These include an iodine-starch test and a thermoregulatory sweat test.
How is it treated?
After any underlying medical condition is ruled out, the focus will be on the excessive sweating. Drugs include:
Prescription Antiperspirant
This antiperspirant contains aluminum chloride. It is applied at bedtime and washed off in the morning.
Prescription Cream
This cream contains glycopyrrolate, which may help hyperhidrosis that affects the face and head.
Nerve-Blocking Medications
Some oral medications prevent the nerves from communicating with each other, which can help with excessive sweating.
Botox Injections
This procedure temporarily blocks the nerves that cause sweating. It can last six to 12 months and then will need to be repeated.
Sometimes surgical treatments may be called for, but they can only be effective for certain areas of the body. For example, sweat gland removal can only be performed in the armpits.
There are things you can do at home to help alleviate the symptoms of hyperhidrosis. These. include over-the-counter antiperspirants and astringents. Both tighten the skin and may help to decrease sweating. Change your socks often and air out your feet. Wear clothes made from natural fibers that allow your skin to breathe. Try relaxation techniques such as yoga, which may help you to avoid the anxieties that trigger excess sweating.
DeSilva Dermatology can counsel you about the condition and suggest treatment options. If you are experiencing excess sweating, call us at (830) 331-4150 for an appointment.

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post